LOADING
Hallux valgus, commonly referred to as a bunion, is a progressive foot deformity that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by a misalignment of the big toe, this condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and mobility issues that impact daily activities. While often associated with ill-fitting footwear, hallux valgus can also stem from genetic factors, structural foot abnormalities, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial in managing this condition effectively. This article explores the various aspects of hallux valgus and provides insight into both non-surgical and surgical interventions to alleviate discomfort and improve foot health.
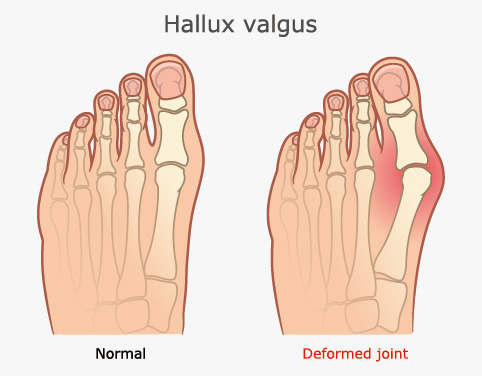
Hallux valgus, commonly known as a bunion, is a foot deformity where the big toe tilts towards the second toe, causing the joint at the base of the big toe (the metatarsophalangeal joint) to protrude outward. This creates a visible bump on the side of the foot, which can lead to discomfort and pain, especially when walking or wearing tight shoes. Hallux valgus is a prevalent condition, with studies estimating that it affects approximately 23 - 35% of adults, particularly among women and older adults.
Hallux valgus can significantly affect an individual’s health and quality of life. The deformity often causes chronic pain, especially during walking or prolonged standing, and can lead to restricted mobility as the misalignment worsens. Finding comfortable footwear becomes challenging due to the protrusion, potentially necessitating specially designed shoes. Additionally, hallux valgus can contribute to secondary foot problems such as corns, calluses, hammertoes, and an increased risk of arthritis. The condition may also impact mental and emotional well-being, as its appearance and associated discomfort can lead to self-consciousness and reduced participation in social or physical activities.
Several factors can contribute to the development of hallux valgus, including:
The symptoms of hallux valgus can vary depending on the severity of the deformity but often include:
Managing hallux valgus typically involves both non-surgical and surgical approaches. Common management strategies include:
Kinesiology taping is a non-invasive method that can help support the muscles and joints in the foot. It works by gently realigning the big toe, reducing strain on the bunion, and providing relief from pain and inflam mation. Taping can also improve foot posture and mobility, making it a useful adjunct to other treatments.

[ To know more about Relief Patch for Toe: Click Here ]

Exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the toes, improve flexibility, and reduce pain associated with hallux valgus. Here are some recommended exercises:

Copy Link