LOADING
Dealing with thumb and wrist pain can be challenging, especially when it interferes with daily activities. One condition that often contributes to this discomfort is De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. This article discusses the causes and treatment options available, focusing on how specialized thumb braces can aid in managing the pain and improving functionality.
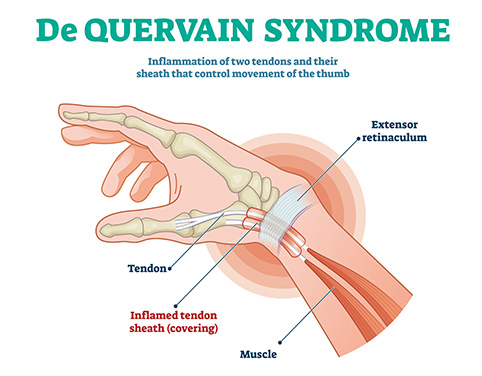
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is a painful condition that involves the swelling and thickening of the tendon sheaths around the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons, which run along the thumb side of the wrist and attach to the base of the thumb. The thickening and swelling of these sheaths cause entrapment of the tendons, resulting in inflammation and pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain and numbness. This condition is typically caused by repetitive hand and wrist movements or overuse and is exacerbated by thumb movement and radial and ulnar deviation of the wrist. (Koehl, 2022; Allbrook, 2019)
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is multifactorial. There are a number of factors that can influence the symptoms, as well as the severity. These factors can include:

The management of de Quervain's tenosynovitis may include (Larsen, 2021; Goel, 2015):
The thumb stabilizer can help immobilize the CMC and MCP joints, reducing the movement and stress on the inflamed tendons that cause de Quervain's tenosynovitis. (Witt, 1991) By reducing movement and stress, the inflammation and pain can decrease, allowing the tendons to heal. (Menendez,2015; Awan,2017) In addition to immobilization, a thumb stabilizer can also provide compression to the affected area, which can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow to the area, aiding in the healing process. The curved design splint of the thumb stabilizer can provide support and keep the thumb in a neutral position without restricting palm or finger movement in daily activities.

Here are some examples of rehabilitation exercises that can help with de Quervain's tenosynovitis:
It is important to perform these exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist or healthcare professional to avoid further injury and ensure proper form and technique.
Copy Link